Company dynamics
Multilayer Paper Filters: Innovation in Filtration Technology
Multilayer Paper Filters: Innovation in Filtration Technology
Introduction
Multilayer paper filters represent a significant advancement in filtration technology, offering enhanced efficiency, versatility, and cost-effectiveness across various industries. These filters are engineered by stacking multiple layers of specialized paper or fiber materials, each designed to perform specific functions such as pre-filtration, fine filtration, and adsorption. This article explores the design principles, applications, advantages, and recent innovations in multilayer paper filter technology.
Design and Structure
Multilayer paper filters typically consist of several distinct layers, each with unique properties tailored to specific filtration needs:
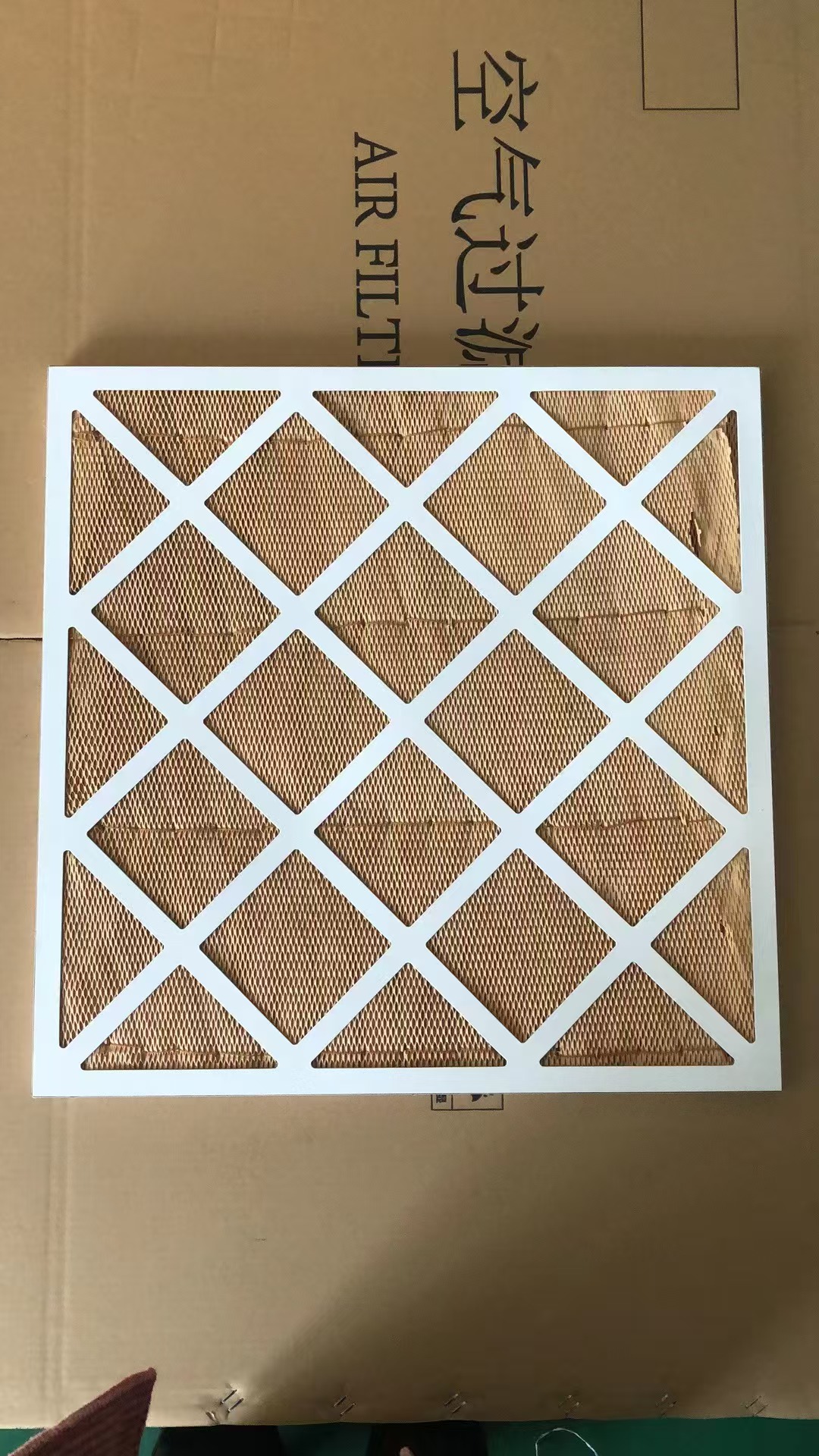
Pre-Filtration Layer: Often made from coarse, porous materials like glass fiber or synthetic non-woven fabrics, this layer captures large particles (e.g., dust, debris) and protects subsequent layers from clogging.
Main Filtration Layer: This layer, sometimes composed of fine glass microfibers or cellulose-based materials, traps smaller particles. For example, filters like the Whatman GMF 150 use a gradient density design, where larger particles are captured in the coarse upper layer, medium-sized particles at the interface, and finer particles in the dense lower layer.
Functional Layers: Additional layers may include activated carbon for adsorbing gases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or odors, and antimicrobial coatings (e.g., silver ions) to inhibit bacterial growth.
The layers are bonded using techniques such as thermal sealing or resin impregnation, ensuring structural integrity without compromising permeability.

Applications
Multilayer paper filters are used in diverse sectors due to their adaptability and efficiency:
Industrial Painting and Coating: Filters like multilayer grid paint filters are essential in spray booths and painting facilities. They capture overspray paint particles, prevent air pollution, and maintain air quality in workplaces. These filters are resistant to solvents and compatible with various paints, including nitrocellulose and epoxy resins.
Environmental and Water Treatment: In water purification, multilayer filters remove sediments, chemicals, and microorganisms. Some designs incorporate ion-exchange resins or activated carbon for heavy metal removal and organic contaminant adsorption.
Air Filtration: HEPA-grade multilayer filters, often made from glass fiber or polypropylene, are used in air purifiers, HVAC systems, and cleanrooms. They achieve efficiencies exceeding 99.97% for particles as small as 0.3 microns.
Laboratory and Pharmaceutical Use: Filters like Whatman GMF 150 are employed in sample preparation, sterile filtration, and analytical processes due to their high particle retention capacity and compatibility with aggressive chemicals.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Multilayer filters are integral to masks and respirators, providing balanced filtration efficiency and breathability. Recent innovations include biodegradable options made from wood pulp.
Advantages
High Efficiency and Capacity: The multilayer design enables progressive filtration, increasing dirt-holding capacity and service life while reducing pressure drop.
Versatility: Filters can be customized in layer composition, size, and geometry (e.g., folded, pleated) to suit specific applications.
Economic and Environmental Benefits: Many multilayer filters are reusable or recyclable. Bio-based materials like wood pulp offer sustainable alternatives to synthetic filters.
Multifunctionality: Combining mechanical filtration with chemical adsorption (e.g., activated carbon) or antimicrobial properties allows all-in-one solutions for complex contamination challenges.
Innovations and Future Directions
Recent research focuses on enhancing performance and sustainability:
Biodegradable Materials: Projects like wood pulp-based multilayer filters for masks aim to reduce plastic waste while maintaining high filtration efficiency (e.g., PM0.3 filtration ≥95% at low resistance).
Smart Filters: Integration of sensors for real-time monitoring of pressure drop or contamination levels is being explored for industrial systems.
Nanotechnology: Incorporating nanofibers or graphene oxide layers could further improve filtration precision and mechanical strength.
Conclusion
Multilayer paper filters are a cornerstone of modern filtration, combining sophisticated design with practical functionality. Their ability to address diverse challenges—from industrial pollution to personal protection—underscores their critical role in health, safety, and environmental sustainability. As technology advances, these filters will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and eco-friendly solutions for a cleaner world.
This article synthesizes insights from industrial products, research patents, and technical specifications to provide a comprehensive overview of multilayer paper filter technology.
Categories
News
Contact Us
Contact: Filter Product Supplier
Phone: +86-15178582688
Tel: 08615178582688
E-mail: edmond@aooluo.com
Add: Dongcheng International, Xinwu Economic Development Zone, Wanzhi District,Wuhu City, Anhui Province, China
 关注官方微信
关注官方微信